Control of blood glucose lesson
- Recap of the structure and function of adrenal glands including location (above the kidneys), different regions and the functions of different regions - LEARN!
- Recap of the role of hormones in negative feedback - every hormone is released from a specific gland and travels in the blood around the entire body. The hormone is detected by certain TARGET CELLS and an EFFECT is produced
- Control of blood glucose is regulated by the hormones GLUCAGON and INSULIN
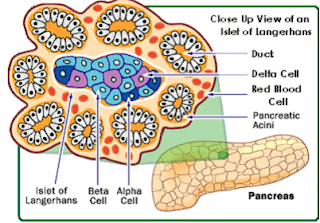
- They are released from the ISLETS OF LANGERHANS in the pancreas
- Glucagon is released when blood glucose levels fall. It effects the liver and results in an INCREASE in the concentration of blood glucose
- Insulin is released when blood glucose levels rise. It effects the liver and results in a DECREASE in the concentration of blood glucose
New associated key words:
GLUCONEOGENESIS: Production of new glucose in the liver and muscle cells from lipid molecules. Stimulated by GLUCAGON
GLYCOGENOLYSIS: The hydrolysis of glycogen in the muscles and liver to release glucose units. Stimulated by INSULIN
GLYCOGENESIS: The production of glycogen from condensation reactions in the muscles and liver. Stimulated by INSULIN
- The cellular basis for insulin release:
HOMEWORK: Complete the booklet by researching the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Complete all exam questions.
- Recap of the role of hormones in negative feedback - every hormone is released from a specific gland and travels in the blood around the entire body. The hormone is detected by certain TARGET CELLS and an EFFECT is produced
- Control of blood glucose is regulated by the hormones GLUCAGON and INSULIN
- They are released from the ISLETS OF LANGERHANS in the pancreas
- Glucagon is released when blood glucose levels fall. It effects the liver and results in an INCREASE in the concentration of blood glucose
- Insulin is released when blood glucose levels rise. It effects the liver and results in a DECREASE in the concentration of blood glucose
New associated key words:
GLUCONEOGENESIS: Production of new glucose in the liver and muscle cells from lipid molecules. Stimulated by GLUCAGON
GLYCOGENOLYSIS: The hydrolysis of glycogen in the muscles and liver to release glucose units. Stimulated by INSULIN
GLYCOGENESIS: The production of glycogen from condensation reactions in the muscles and liver. Stimulated by INSULIN
- The cellular basis for insulin release:
HOMEWORK: Complete the booklet by researching the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Complete all exam questions.



Comments
Post a Comment