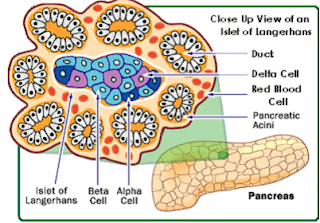
- Summary of ecothermy and endothermy including adaptations to these lifestyles FOR EXAMPLE: Many reptiles with bask in the sun to increase their body temperature in the morning which enables them to become more active - Introduction of key words relating to the topic including: endocrine gland, exocrine gland, target organ, hormone, protein hormone, lipid hormone - Explanation of the different modes of action of protein hormones vs. lipid hormones - PROTEIN HORMONES - protein hormones bind to cell surface receptors and initiate G proteins which activates adenyl cyclase producing the second messenger cAMP - STEROID HORMONES - diffuse directly across the membrane and bind with receptor molecules in the cytoplasm forming hormone-receptor complexes. These then cross into the nucleus and act as transcription factors HOMEWORK - 1. revise for the mock exam! 2. Write an essay explaining how the release of insulin is controlled and how this helps to regulat...